Docker image¶
We can easily build a docker image using the following Dockerfile:
# **************************************************************************
# Purpose ...: jfricas (https://github.com/fricas/jfricas)
# Build .... : docker build -t jfricas:latest .
# Test ..... : docker run -ti --rm --network=host
# --env DISPLAY=:0 fricas/jfricas:latest jupyter notebook
# Version .. : 0.2.17 -- 17-SEP-2019
# OS ....... : ubuntu:latest
# FriCAS ... : fricas:latest
# **************************************************************************
FROM fricas/fricas
LABEL fricas-devel <fricas-devel@googlegroups.com>
# ENV DEBIAN_FRONTEND noninteractive
# discouraged: see https://docs.docker.com/engine/faq/
ENV JFRICAS_GITHUB https://github.com/fricas/jfricas
ENV JFRICAS_VERSION 0.2.17
# ======================================
# Get packages and install missing tools
# ======================================
RUN apt-get update && apt-get install -y -q \
python3.6 \
python3-pip \
cl-asdf \
cl-hunchentoot \
firefox \
gnuplot
# ===============================
# Install jfricas.pip from Github
# ===============================
RUN cd /root && \
pip3 install jupyter && \
git clone $JFRICAS_GITHUB && \
cd jfricas && \
pip3 install . && \
python3 -m jfricas.install_kernel && \
cd /root
Build¶
Go to the directory containing the Dockerfile and type
docker build -t jfricas:latest .
or with logfile:
docker build -t jfricas:latest . > log
Alternatively you want to use the build.sh script:
#!/bin/sh
sudo docker rmi fricas/jfricas:latest
sudo docker build -t fricas/jfricas:latest . > log
sudo docker images
Test¶
There is a test.sh in the docker subfolder, or you can enter the command
by hand (one line, otherwise use line continuation):
docker run -ti --rm --network=host --env DISPLAY=:0 fricas/jfricas:latest
jupyter notebook --no-browser --allow-root
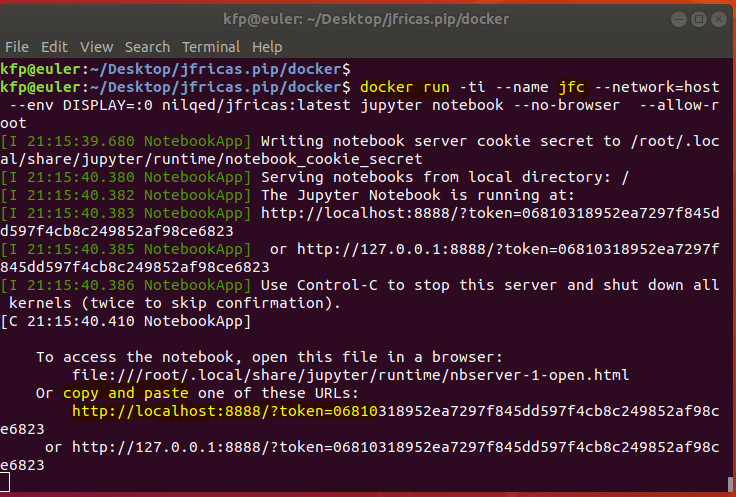
To merely access the container you can also use
docker run -ti --rm fricas/jfricas:latest /bin/bash
to get a bash, from where you can start things manually.
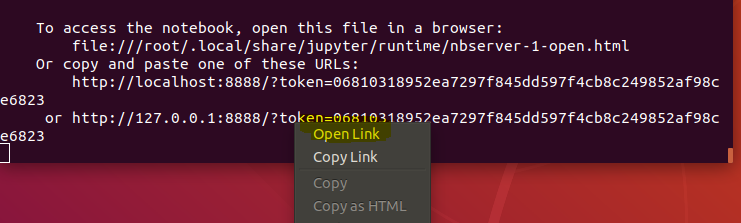
Right click on a link and choose open.
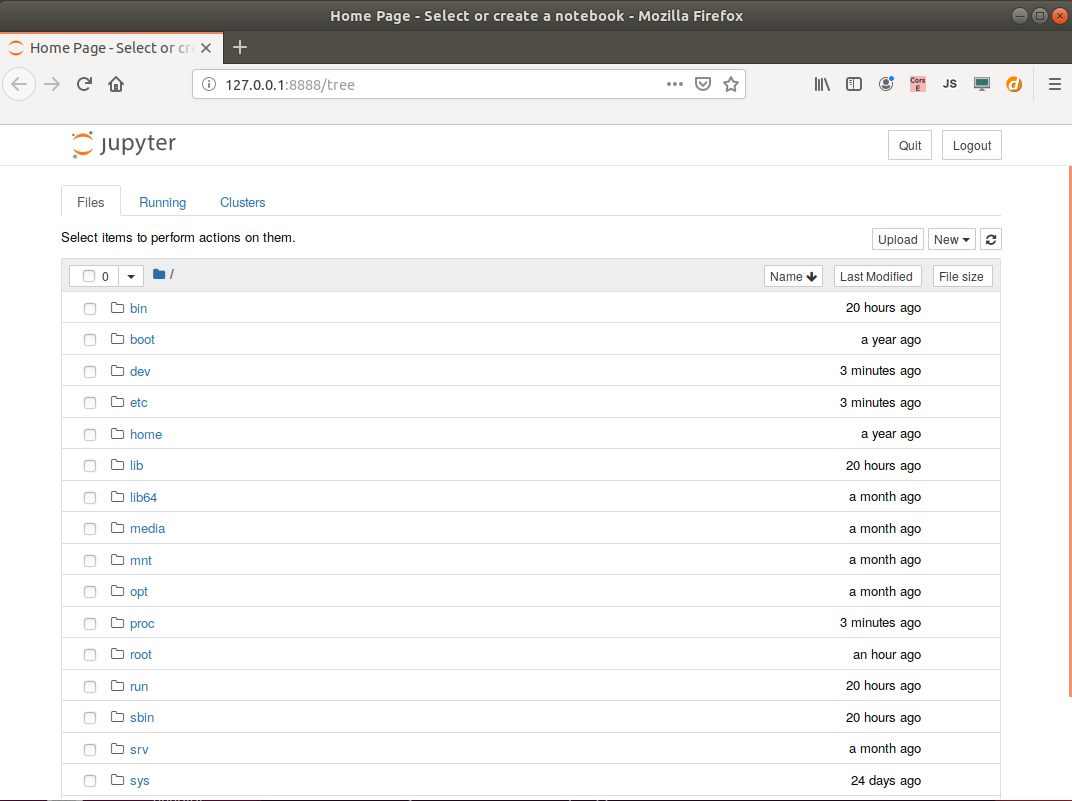
Your browser should open and display the root directory of the image.
Choose the kernel by New->FriCAS
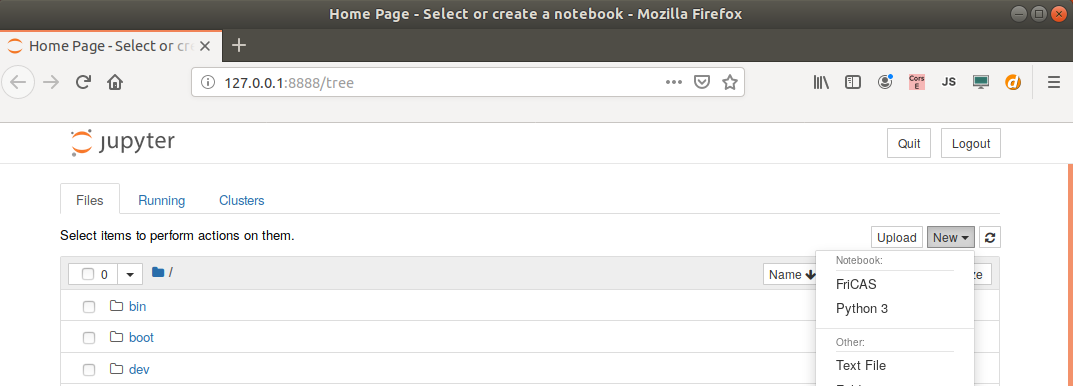
then you can use the notebook:
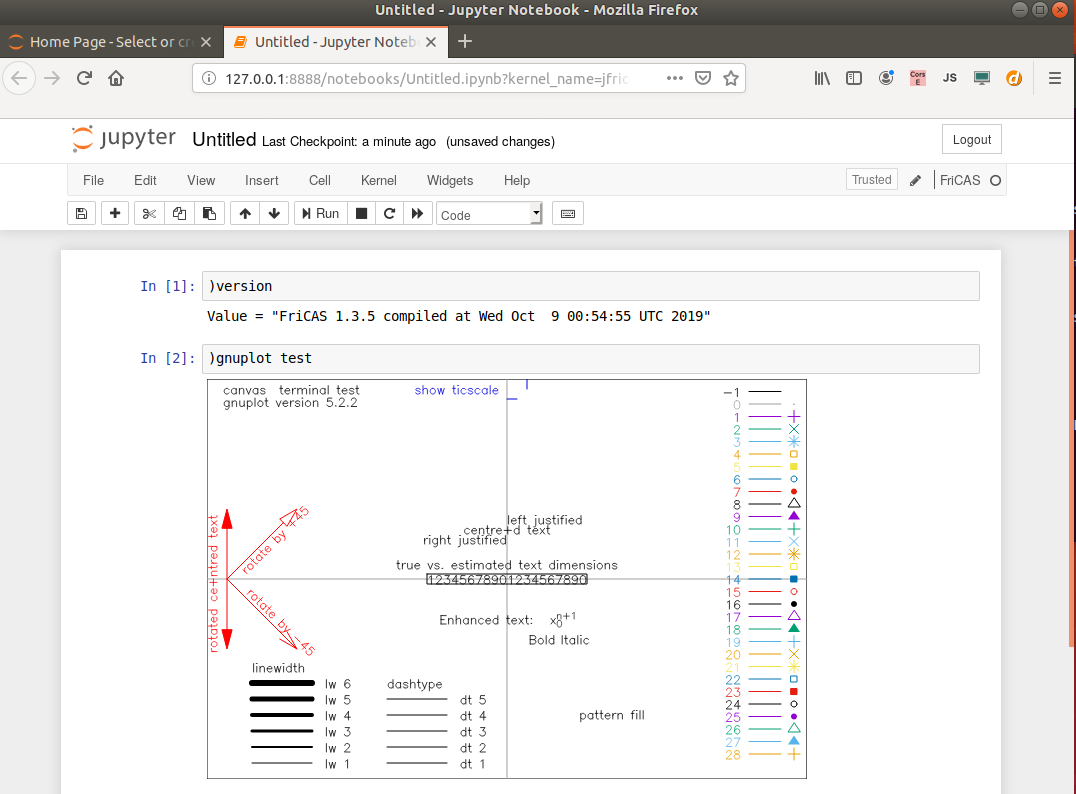
Note: the --rm option means that the container is deleted after closing
the notebook server. This is for testing only, so that your computer will
not populated with a lot of orphaned containers. If you want to save your
work (*.ipynb, etc.), then remove --rm and use --name for named
containers if you like.
Push¶
To push the image you can use the script push.sh, or the command:
sudo docker push fricas/jfricas:latest
RUN¶
There are two scripts: run.sh and runx.sh which may be used to start
the jupyter notebook inside the jfricas docker image. The latter can
be used if you want to have Hyperdoc and Draw, otherwise run.sh
is safer as it will not set any permissions (xhost local:root).
Example for running a named container (jfc):
docker run -ti --name jfc --network=host
--env DISPLAY=:0 fricas/jfricas:latest
jupyter notebook --no-browser --allow-root
To save the changes in jfc to the image, do
sudo docker commit jfc fricas/jfricas
[sudo] password for user:
sha256:bea4f6525c7b2f03f6893bec5a03646a1ba69cb8f669890c14105fa61010c1dd
Then you can remove the `jfc container (if you like):
docker rm jfc
Do not forget do push the changed image (only if you want to, of course):
sudo docker push fricas/jfricas
The commands docker ps -a will list all active containers, while
docker images will show the images.